Web content filtering is critical for protecting networks and users against web-based threats, inappropriate internet content, and distracting websites. With all of the options for controlling internet access you may be wondering: what is the best internet filter?
In this article I will overview solutions for web content filtering, describe the different methods of controlling internet access, and emphasize the importance of blocking certain websites.
Table of ContentsWhat Is Web Content Filtering?
Web content filtering is the process of preventing employees, students, and other end-users from accessing content on the internet. The most common content to block are websites that are offensive, inappropriate, or high-risk. Schools and businesses use tools such as web content filtering software to block access to these websites.
Why Is Web Content Filtering Important?

- Employee Internet Management (EIM): Web filters enable organizations to regulate their employee’s access to undesirable websites. This is essential for managing compliance requirements, bandwidth usage, or other business concerns.
- CIPA Compliance: US-based schools and libraries that wish to receive valuable e-Rate discounts need to use web content filters to prevent minors from being exposed to obscene visual content.
- Bandwidth Management: Network performance can be dramatically reduced by the overuse of bandwidth hogging sites like YouTube and Twitch. These websites can be blocked or restricted to help reduce bandwidth usage.
- Cybersecurity: Web content filters improve security by blocking access to websites that are high-risk or known to be dangerous. Data leakage can also be prevented by blocking cloud storage sites and P2P file sharing services.
- Productivity Management: Web content filters block access to distracting websites such as social media sites, computer games platforms, and video streaming services.
- Legal Liability: Web content filtering is essential for preventing access to content that is inappropriate such as porn, grotesque imagery, violence, and profanity. These filters prevent underaged users from accessing adult content and reduce the potential for internet abuse to cause a hostile work environment.
4 Types of Web Content Filtering
Keyword Filtering

Keyword-based web content filtering blocks end-users from connecting to websites that have specific keywords. These keywords are identified using regular expressions (regex) and/or a predefined list of blocked keywords.
The intention of using keywords for web filtering is to prevent users from accessing inappropriate content, however due to the Scunthorpe problem (keyword filters falsely flagging content) keyword filtering has a high potential to block access to legitimate websites. For this reason category-based web filters that include adult-oriented categories are typically used instead.
Web Category Filtering

Web category filtering is used to block websites based on content categories such as pornography, violence, hate, and social media. To do this the web filtering software references a centralized database that associates websites with common categories.
These databases need to be constantly updated to keep up with new websites as they are created. For this reason the web category filtering database is most often provided by the vendor of the web filtering solution.
URL Filtering

When you want to access a specific webpage, you will type in a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) into your address bar such as CurrentWare.com or CurrentWare.com/blog. URL filtering blocks or allows access to specific websites or web pages based on these URLs.
URL filtering provides more granular and detailed filtering than DNS filtering by allowing companies to block individual web pages instead of the whole website at once. To make blocking entire websites easier URL-based web filters may also allow for wildcard filtering, which blocks the entire website unless exceptions are added to an allow list.
For example, a wildcard-supporting URL filter with “Facebook” on its block list and Facebook.com/CompanyPage on its allow list will allow access to Facebook.com/CompanyPage and stop users from accessing any other Facebook link.
How Does URL Filtering Work?
With reference to the Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model), a URL filter blocks websites using the packet information sent during the TCP/UDP protocol (layer 4, the transport layer) or by examining the URL in the address bar of the web browser (layer 7, the application layer).
DNS Filtering
From an end-user perspective blocking websites using a Domain Name System (DNS) filter is similar to filtering using a URL filter. Both solutions allow you to enter a website into the block list of the web filtering software in order to prevent access to the website.
The key differences are:
- DNS filtering can’t block access to websites based on URL; instead, it blocks entire domains.
- A DNS filter requires all internet traffic to be forwarded to an external DNS server provided by a web filtering service provider.
- The URL web filter acts directly on HTTP/HTTPS traffic, while DNS filtering acts on the initial DNS queries that precede the HTTP/HTTPS connection attempts.
To understand how DNS filtering works, it’s important to understand how DNS is used when visiting a website. The human-readable URLs that we type into our web browsers are moreso there for our convenience; the process of connecting to a website actually resolves to an IP address that is associated with a web server that hosts the desired domain.
When we attempt to access a website, the DNS is used to locate the server where the domain’s website is located. A DNS filter blocks access to websites by intercepting the initial DNS query.
The filter will use its own DNS resolving service to determine whether or not the DNS query will be allowed to continue. If the domain of the desired website is not permitted on the network the website will not be served and the user will be redirected to an alternative page with a warning message.
As these IP addresses are mapped to an entire domain (website), DNS filtering does not allow you to selectively block individual pages. For example, if you would like to block access to Facebook while still allowing access to your company’s Facebook page you will not be able to do that.
For a detailed description of the DNS lookup process, check out this explainer from VeriSign.
5 Web Content Filtering Technologies
Browser-Based Filters

Browser-based site blockers are extensions, applications or add-ons that are specific to each individual browser. They are most often used by individuals that would like to block distracting websites. These filters are rarely used in business settings as they are easy to bypass by using another browser.
Search Engine Filters

Search engines typically include some method of filtering out explicit search results. These filters allow for search engines to be used in environments where adult-oriented content would be considered inappropriate such as schools, public libraries, and most workplaces.
Inline Web Filters

Inline web filters are software or hardware appliances (such as an internet gateway) that operate within the network that they are filtering. These solutions are installed as a gateway that directly intercepts all traffic that travels through the network.
As they do not require a software client to be installed on each endpoint they are often used in environments that have guest networks, mixed platform devices, or other circumstances where direct control over devices is not feasible.
While the lack of a software client is advantageous for some deployments, it comes with a few tradeoffs. If access to a specific website is blocked in an inline filter it must remain blocked for all users on the network. These solutions are also not ideal for managing the devices of remote workers as the filtering only applies when they are connected to the network.
Endpoint-Based Web Filters

Endpoint-based web filters such as BrowseControl have a software client that allow web filtering policies to be customized on a per-user or per-device basis. The software clients receive web filtering policy updates from a central server that is managed by the company and retain the policies even when the devices disconnect from the network.
Since a software client needs to be installed on each device that will be controlled, organizations with a large number of devices will leverage automated software deployment tools that install the agent on all of their devices simultaneously.
The need for a dedicated software agent also means that endpoint-based web filters are best used in environments that have in-office or remote workers using company-provided devices. Employees using personal devices for work-related tasks may object to having software installed on their devices.
Firewalls
Firewalls are a type of inline web content filter. Firewalls can be hardware appliances or cloud-based/software-based virtual appliances. Rather than blocking specific websites, firewalls filter network traffic to authorized ports, protocols, and IP addresses.
Traditional packet-filtering firewalls operate at layer 3 (the network layer) of the OSI model to filter ports, protocols, and IP addresses. While these types of firewalls do block web traffic, they lack the ability to distinguish between specific websites as they cannot identify URLs or domain names.
Over time traditional firewalls have evolved into “Next Generation Firewalls” (NGFW) that combine the packet filtering of traditional firewalls with other network filtering functions such as web application firewalls (WAFs), web content filters, and intrusion prevention systems. These solutions are typically used to harden networks and block internet traffic that has been identified as malicious.
Unless you are using a next generation firewall (NGFW) with an integrated web filter that allows you to block specific URLs, a dedicated web filter is going to give you far more granularity for controlling access to websites.
What Web Content Filter Should You Use?
What is considered the best web content filter depends on the needs of your environment. In many environments it is not uncommon to see multiple forms of web content filtering in place that meet different requirements.
For example, a business with dedicated office space could use an inline firewall to control ingress and egress traffic as it goes through their network while also using an endpoint-based URL filter to control what specific websites their employees can access.
To simplify the comparison this section will focus on two common tools for controlling the websites that employees can access: Inline network-based DNS filtering vs endpoint-based URL filtering with a software agent.
| Inline Web Filter (Agentless) | Endpoint Web Filter (Agent) | |
| Allow/Block Domains | ||
| Allow/Block URLs | ||
| Custom filtering profiles for each user/device | ||
| Block website categories | ||
| Manage guest/unknown devices | ||
| Web filtering schedules | ||
| Category filtering | ||
| Block websites on any network |
Level of Control (Granularity)
The key difference between DNS filtering and URL filtering is that DNS filtering blocks entire websites based on DNS queries rather than specific URLs. DNS filtering will allow you to block undesirable domains for your entire network, however it lacks the ability to block a website while allowing individual web pages.
This can be problematic in an environment where users, computers, or departments require different levels of access. Examples include business environments where marketing staff need work-related access to social media or educational environments where students and staff need unique web filtering policies.
In environments where user-level or device-level control is desired the best internet filter will be one that supports unique filtering profiles for each user or device.
Remote Workforce Management

Agent-based web filters are the best web filter for remote workers as they will block websites even when they disconnect from the company network. This is ideal for other scenarios that have employees working offsite, such as laptop users that need to be protected when a corporate device is used at a remote site.
Agent-based web filters also provide the means to apply different allowed and blocked lists on a set schedule. This allows employees to access non-work websites after work hours in environments where employees are allowed to use company-provided equipment for personal use.
For BYOD environments, employees that use personal computers for work may not feel comfortable allowing their employers to install web filtering software clients on their devices. In this instance an inline DNS filter can be installed on the company network or a client-based filter can be installed on the computer that they remotely connect to. However, added security controls must be in place to mitigate the risks of allowing non-managed devices to connect to the corporate network.
Block Websites Based on Categories

Category filtering is a must-have feature for restricting access to inappropriate content. Fortunately, both DNS-based and URL-based web filtering software providers offer this feature. With category filtering you can leverage a pre populated database of websites that you can block rather than manually sourcing your own list of websites.
DNS-based solutions with category filtering will only be able to strictly block or allow the entire category for your network. If you would like to block the social media category for the majority of your users while still allowing access for your marketing team you will need URL filtering.
Monitoring Web Activity

Web filters only block what they are told to block. This leaves opportunities for end-users to access undesirable websites that have not yet been added to the web filter. Though many web filtering solutions will include some form of logging or auditing to identify the websites that are being visited, using web content filtering in tandem with a dedicated internet monitoring software is the ideal solution for enforcing acceptable use policies and ensuring that the internet is being used appropriately.
Guest Networks

If you would like to set up web filtering on a network where you will not have direct control over the devices that connect to it (such as a guest WiFi hotspot), you need a network-level web content filtering solution. An agent-based solution is not ideal in this scenario as there is no feasible way to install the agent on non-managed devices.
How to Block Websites With BrowseControl
BrowseControl makes controlling internet access based on users, departments, and computers incredibly easy. Once you’ve installed the software all it takes is just a few clicks to set up user-based permissions. This tutorial will guide you through the general setup process and show you how to control internet access based on users with BrowseControl.
Setup File Contents:
- CurrentWare Server and Console Setup File (CurrentWare.exe)
- CurrentWare Client Setup File (cwClientSetup.exe)
Install the CurrentWare Console on the manager’s computer
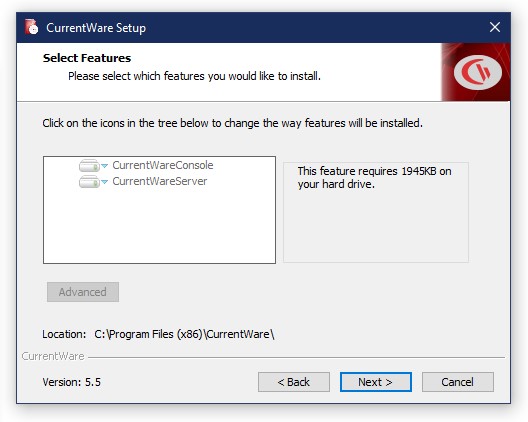
- Launch the CurrentWare Console setup file (CurrentWare.exe)
- Read and accept the End-User License Agreement (EULA)
- Select “CurrentWareConsole” and click “Next”
- Select BrowseControl and Category Filtering solutions
- The Installer will proceed to install the CurrentWare Server, Console and BrowseControl onto the manager’s computer. This process will take 3-5 minutes to complete.
Note: For companies installing BrowseControl on more than 300 computers, we recommend installing the CurrentWare Client setup file on a server and using SQL Server Professional as the database. To see Remote Deployment Options for BrowseControl, visit our quick-start installation page.
Install the CurrentWare Clients on the computers you would like to control

- Take the CurrentWare Client setup file (cwClientSetup.exe) and launch it on the computers that you would like to block websites on.
- The installer will ask you for the name of the computer that the CurrentWare console is installed on from step 1. Advanced users can also use the IP address of their CurrentWare Server.
- For instructions on how to find the name of the computer that you installed the CurrentWare Console on you can visit our video tutorial or see the Microsoft support page.
- After the CurrentWare Client installation is complete, it will connect to your CurrentWare Console (the manager’s computer from step 1) automatically.
- Repeat this process on all the computers you would like to control with the BrowseControl software.
Launch the CurrentWare Console on the managing computer

Now you can start to control internet access based on users using BrowseControl. You can control internet access in one of three ways:
- Block a small number of specific websites based on their URL
- Block websites based on category
- Block all websites except for pre-approved websites
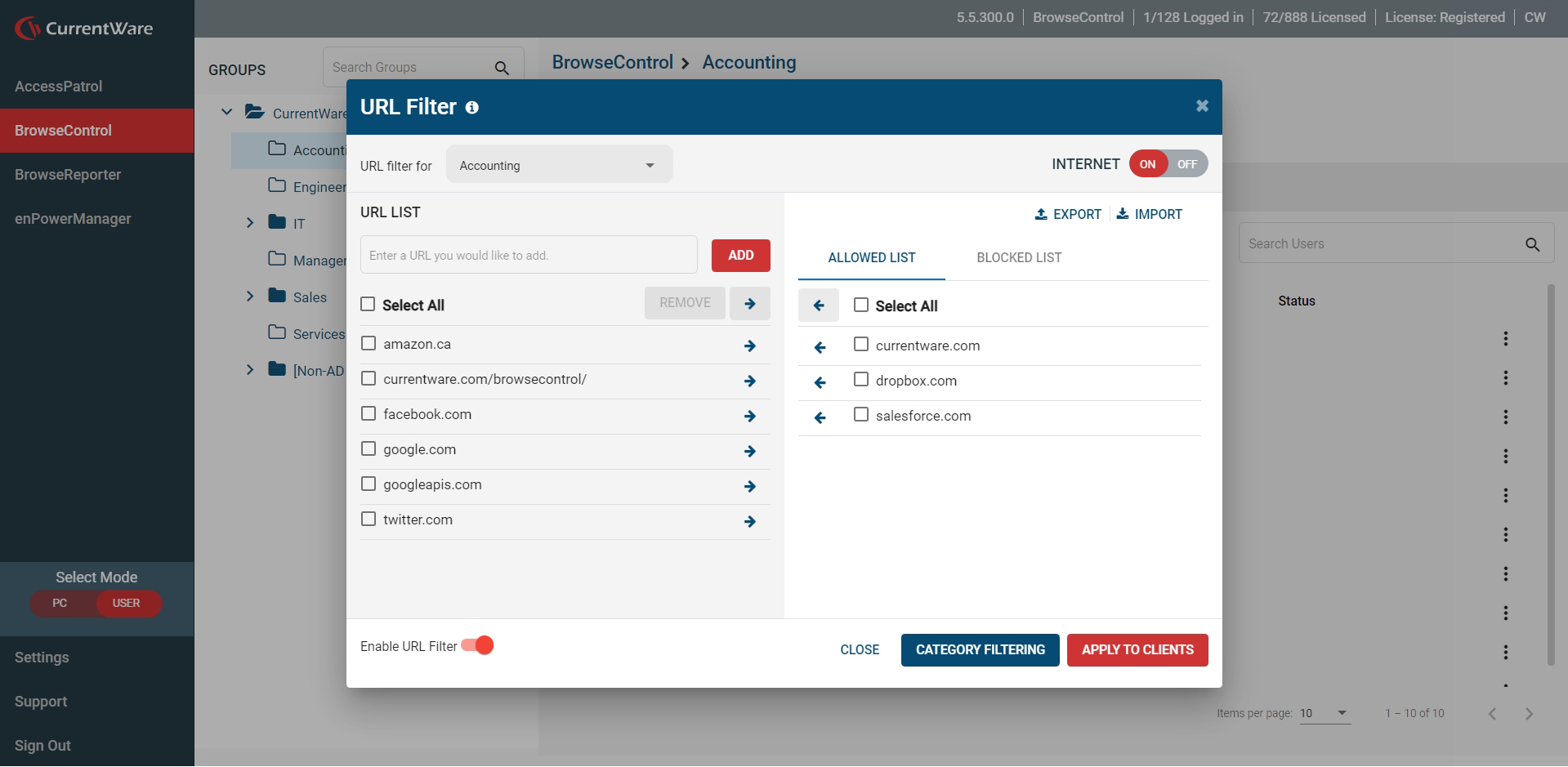
How to block websites by URL

- Select the user(s) that you would like to apply the policy to
- Set “Internet” to “On” if it is not already on
- Go to “URL Filter”
- Add the URL (www.NameOfWebsiteToBlock.com) of the website you would like to block to the URL list
- Select “Blocked List”
- Click the checkbox next to the desired URL and then click “Add to Blocked List”
- Click “Apply to Clients” to deploy the web filtering policy
How to block websites by category

With BrowseControl’s category filtering feature you can easily block millions of websites across hundreds of predefined categories. In just a few clicks you can prevent users from accessing social media, pornography, and other undesirable categories of websites.
- Select the user(s) that you would like to apply the policy to
- Set “Internet” to “On” if it is not already on
- Go to “Category Filtering”
- Add the categories you would like to block (ex. “Social Media”) to the Blocked Category List
How to only allow access to specific websites
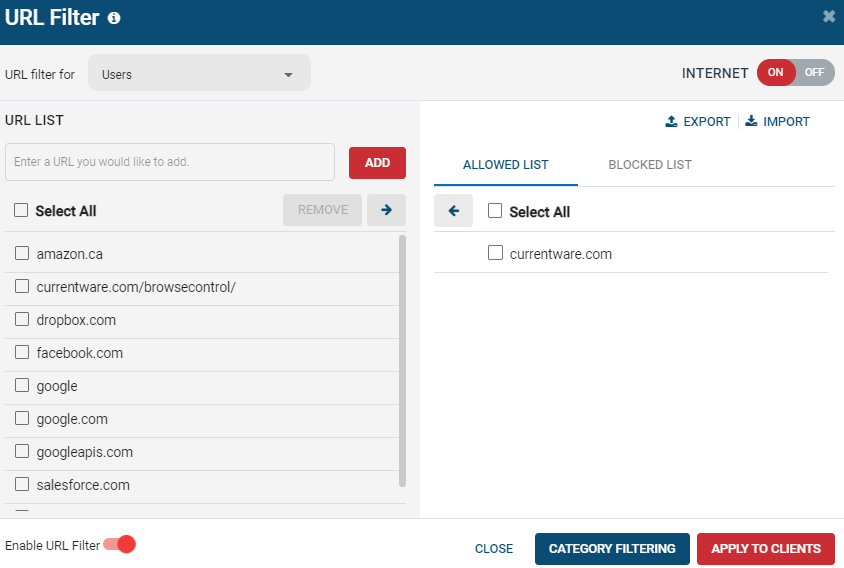
If you would like to limit internet access to a pre-authorized list of websites, you can easily do that in BrowseControl.
- Select the user(s) that you would like to apply the policy to
- Set “Internet” to “Off”
- Go to “URL Filter”
- Add the allowed websites to the Allowed List
Conclusion
Controlling access to the internet is a critical component of organizational security, productivity management, and acceptable use policy enforcement. The best internet filter will depend on the needs of your environment, the devices you would like to control, and the level of granularity desired.
Ready to control internet access? Get started with a FREE 14-day trial of BrowseControl, CurrentWare’s web content filtering software.
The post Web Content Filtering: What’s the Best Way to Block Websites? appeared first on CurrentWare.